In another new whitepaper on 5G-Advanced, Nokia has detailed DCCA (DC + CA) features and enhancements from Rel-15 until Rel-18. The following is an extract from the paper:
Mobility is one of the essential components of 5G-Advanced. 3GPP has already defined a set of functionalities and features that will be a part of the 5G-Advanced Release 18 package. These functionalities can be grouped into four areas: providing new levels of experience, network extension into new areas, mobile network expansion beyond connectivity, and providing operational support excellence. Mobility enhancements in Release 18 will be an important part of the ‘Experience enhancements” block of features, with the goal of reducing interruption time and improving mobility robustness.
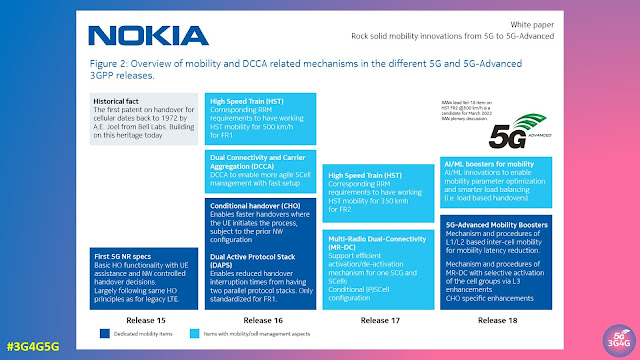
Fig. 2 shows a high-level schematic of mobility and dual connectivity (DC)/Carrier Aggregation (CA) related mechanisms that are introduced in the different 5G legacy releases towards 5G-Advanced in Release 18. Innovations such as Conditional Handover (CHO) and dual active protocol stack (DAPS) are introduced in Release 16. More efficient operation of carrier aggregation (CA), dual connectivity (DC), and the combination of those denoted as DCCA, as well as Multi-Radio Access Technology DC (MR-DC) are introduced through Releases 16 and 17.
For harvesting the full benefits of CA/DC techniques, it is important to have an agile framework where secondary cell(s) are timely identified and configured to the UE when needed. This is of importance for non-standalone (NSA) deployments where a carrier on NR should be quickly configured and activated to take advantage of 5G. Similarly, it is of importance for standalone (SA) cases where e.g. a UE with its Primary Cell (PCell) on NR Frequency Range 1 (FR1) wants to take additional carriers, either on FR1 and/or FR2 bands, into use. Thus, there is a need to support cases where the aggregated carriers are either from the same or difference sites. The management of such additional carriers for a UE shall be highly agile in line with the user traffic and QoS demands; quickly enabling usage of additional carriers when needed and again quickly released when no longer demanded to avoid unnecessary processing at the UE and to reduce its energy consumption. This is of particular importance for users with time-varying traffic demands (aka burst traffic conditions).
In the following, we describe how such carrier management is gradually improved by introducing enhancements for cell identification, RRM measurements and reduced reporting delays from UEs. As well as innovations related to Conditional PSCell Addition and Change (CPAC) and deactivation of secondary cell groups are outlined.
The paper goes on to discuss the following scenarios in detail for DCCA enhancements:
- Early measurement reporting
- Secondary cell (SCell) activation time improvements
- Direct SCell activation
- Temporary RS (TRS)-based SCell Activation
- Conditional Secondary Node (SN) addition and change for fast access
- Activation of secondary cell group
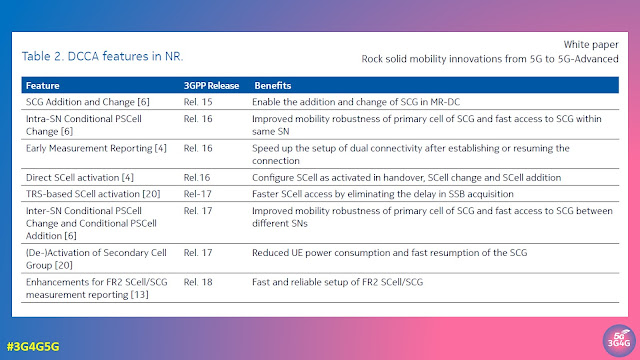
The table below summarizes the DCCA features in 5G NR
Related Posts:
- The 3G4G Blog: ATIS Webinar on '5G Standards Development Update in 3GPP Release 17 and 18'
- The 3G4G Blog: 3GPP's 5G-Advanced Workshop Summary
- The 3G4G Blog: What Is the Role of AI and ML in the Open RAN and 5G Future?
- The 3G4G Blog: Conditional Handover (Rel. 16) Explained
- The 3G4G Blog: Understanding the Dual Active Protocol Stack (DAPS) Handover in 5G
- Free 6G Training: Deep Learning in the 6G Air Interface
- Free 6G Training: Kyocera Develops Transmissive Metasurface Technology for B5G and 6G
- Free 6G Training: 6G and B5G Prospects for Vertical Industry
- Free 6G Training: The Potential of Full Duplex in Beyond 5G and 6G
- Free 6G Training: Using a Dielectric Waveguide as a Pinching Antenna for B5G and 6G