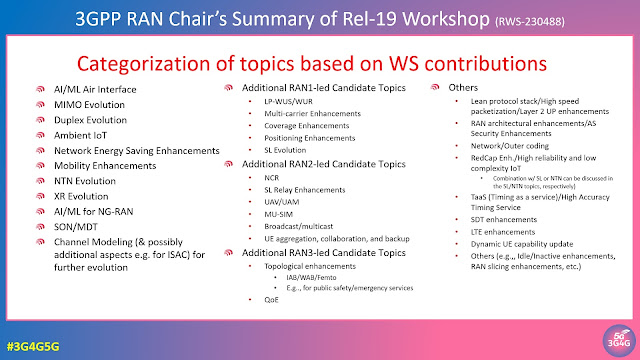
When talking about mobile networks, we generally talk about disaggregation and virtualization of the RAN rather than the core. The 5G Core Network was also designed with disaggregation in mind, supporting service-based architecture (SBA) where Network Functions (NFs) are modular and can be deployed as microservices.
The 5G Core (5GC) is the foundation for Standalone 5G (5G SA) networks where the end users can experience the power of 'real' 5G. A newly published forecast report by Dell’Oro Group pointed out that the Mobile Core Network (MCN) market 5-year cumulative revenue forecast is expected to decline 10 percent (2024-2028). The reduction in the forecast is caused by severe economic headwinds, primarily the high inflation rates, and the slow adoption of 5G SA networks by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs).
While most people think of 5G Core Network as a single entity, in reality it contains many different network functions that can be supplied by different vendors. One way to select the vendors is based on grouping of NFs based on functionality as shown in the picture above. Here we have categorised them into User Plane & Mobility, Subscriber Data Management, Routing & Selection, and Policy & Charging.
An example of of this disaggregation can be seen in the image above where Telenor worked with partners to build a truly multi-vendor, 5G core environment running on a vendor-neutral platform. According to their announcement:
“The main component of 5G-SA is the 5G mobile core, the ‘brain’ of the 5G system. Unfortunately, most 5G core deployments are still single vendor dependent, with strong dependencies on that vendor’s underlying proprietary architecture. This single-vendor dependency can be a killer for innovation. It restricts open collaboration from the broader 5G ecosystem of companies developing new technology, use cases, and services that the market expects,” explains Patrick Waldemar, Vice President and Head of Technology in Telenor Research.
As an industry first, Telenor, along with partners, have established to build a truly multi-vendor, 5G core environment running on a vendor-neutral platform. The multi-vendor environment consists of best of breed Network Functions from Oracle, Casa-Systems, Enea and Kaloom, all running on Red Hat Openshift, the industry’s leading enterprise Kubernetes platform.
“To protect the 5G infrastructure from cyber threats, we deployed Palo Alto Networks Prisma Cloud Compute, and their Next Generation Firewall is also securing Internet connectivity for mobile devices. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform is being used as a scalable automation system, while Emblasoft is providing automated network testing capabilities. The 5G New Radio (NR) is from Huawei,” says Waldemar.
In their whitepaper on "How to build the best 5G core", Oracle does a very similar grouping of the NFs like the way I have shown at the top and highlights what they supply and which partner NFs they use.
When the mobile operator Orange announced the selection of suppliers for their 5G SA networks in Europe, the press release said the following:
Orange has chosen the following industrial partners:
- Ericsson’s 5G SA core network for Belgium, Spain, Luxembourg and Poland
- Nokia’s 5G SA core network for France and Slovakia
- Nokia’s Subscriber Data Management for all countries
- Oracle Communications for 5G core signaling and routing in all countries
Finally, I have depicted four scenarios for deployment and which Cloud Native Environment (CNE) would be used. In a single vendor core, the CNE, even though from a third party, could belong to either the vendor themselves (scenario 1) or may be suggested by the operator (scenario 2).
In case of a multi-vendor deployment, it is very likely that each vendor would use their own CNE (scenario 4) rather than one suggested by the operator or belonging to the lead vendor (scenario 3).
If you have been involved in trial/test/deployment of a multi-vendor 5G Core, would love to hear your feedback on that as well as this post.
Related Posts:


_April2021.jpg)