I realised that I have not looked at Positioning techniques a lot in our blogs so this one should be a good summary of the latest positioning techniques in 5G.
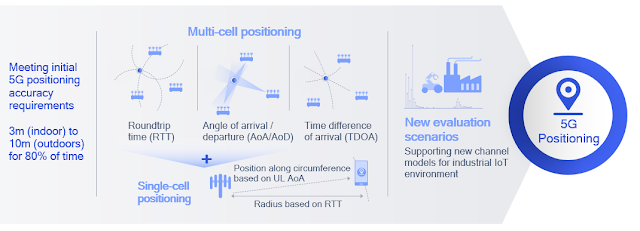
Qualcomm has a nice short summary here: Release 16 supports multi-/single-cell and device-based positioning, defining a new positioning reference signal (PRS) used by various 5G positioning techniques such as roundtrip time (RTT), angle of arrival/departure (AoA/AoD), and time difference of arrival (TDOA). Roundtrip time (RTT) based positioning removes the requirement of tight network timing synchronization across nodes (as needed in legacy techniques such as TDOA) and offers additional flexibility in network deployment and maintenance. These techniques are designed to meet initial 5G requirements of 3 and 10 meters for indoor and outdoor use cases, respectively. In Release 17, precise indoor positioning functionality will bring sub-meter accuracy for industrial IoT use cases.I wrote about the 5G Americas white paper titled, "The 5G Evolution: 3GPP Releases 16-17" highlighting new features in 5G that will define the next phase of 5G network deployments across the globe. The following is from that whitepaper:
Release-15 NR provides support for RAT-independent positioning techniques and Observed Time Difference Of Arrival (OTDOA) on LTE carriers. Release 16 extends NR to provide native positioning support by introducing RAT-dependent positioning schemes. These support regulatory and commercial use cases with more stringent requirements on latency and accuracy of positioning.25 NR enhanced capabilities provide valuable, enhanced location capabilities. Location accuracy and latency of positioning schemes improve by using wide signal bandwidth in FR1 and FR2. Furthermore, new schemes based on angular/spatial domain are developed to mitigate synchronization errors by exploiting massive antenna systems.
The positioning requirements for regulatory (e.g. E911) and commercial applications are described in 3GPP TR 38.855. For regulatory use cases, the following are the minimum performance requirements:
- Horizontal positioning accuracy better than 50 meters for 80% of the UEs.
- Vertical positioning accuracy better than 5 meters for 80% of the UEs.
- End-to-end latency less than 30 seconds.
For commercial use cases, for which the positioning requirements are more stringent, the following are the starting-point performance targets
- Horizontal positioning accuracy better than 3 meters (indoors) and 10 meters (outdoors) for 80% of the UEs.
- Vertical positioning accuracy better than 3 meters (indoors and outdoors) for 80% of the UEs.
- End-to-end latency less than 1 second.
Figure 3.11 above shows the RAT-dependent NR positioning schemes being considered for standardization in Release 16:
- Downlink time difference of arrival (DL-TDOA): A new reference signal known as the positioning reference signal (PRS) is introduced in Release 16 for the UE to perform downlink reference signal time difference (DL RSTD) measurements for each base station’s PRSs. These measurements are reported to the location server.
- Uplink time difference of arrival (UL-TDOA): The Release-16 sounding reference signal (SRS) is enhanced to allow each base station to measure the uplink relative time of arrival (UL-RTOA) and report the measurements to the location server.
- Downlink angle-of-departure (DL-AoD): The UE measures the downlink reference signal receive power (DL RSRP) per beam/gNB. Measurement reports are used to determine the AoD based on UE beam location for each gNB. The location server then uses the AoDs to estimate the UE position.
- Uplink angle-of-arrival (UL-AOA): The gNB measures the angle-of-arrival based on the beam the UE is located in. Measurement reports are sent to the location server.
- Multi-cell round trip time (RTT): The gNB and UE perform Rx-Tx time difference measurement for the signal of each cell. The measurement reports from the UE and gNBs are sent to the location server to determine the round trip time of each cell and derive the UE position.
- Enhanced cell ID (E-CID). This is based on RRM measurements (e.g. DL RSRP) of each gNB at the UE. The measurement reports are sent to the location server.
UE-based measurement reports for positioning:
- Downlink reference signal reference power (DL RSRP) per beam/gNB
- Downlink reference signal time difference (DL RSTD)
- UE RX-TX time difference
gNB-based measurement reports for positioning:
- Uplink angle-of-arrival (UL-AoA)
- Uplink reference-signal receive power (UL-RSRP)
- UL relative time of arrival (UL-RTOA)
- gNB RX-TX time difference
NR adopts a solution similar to that of LTE LPPa for Broadcast Assistance Data Delivery, which provides support for A-GNSS, RTK and OTDOA positioning methods. PPP-PTK positioning will extend LPP A-GNSS assistance data message based on compact “SSR messages” from QZSS interface specifications. UE-based RAT-dependent DL-only positioning techniques are supported, where the positioning estimation will be done at the UE-based on assistance data provided by the location server.
Related Posts:
- Connectivity Technology Blog: 5G Indoor Precise Positioning
- The 3G4G Blog: R&S Webinar on LTE-A Pro and evolution to 5G