The GSMA Mobile Economy report series provides the latest insights on the state of the mobile industry worldwide. Produced by GSMA's in-house research team, GSMA Intelligence, these reports contain a range of technology, socio-economic and financial datasets, including forecasts out to 2025. The global version of the report is published annually at MWC Barcelona, while regional editions are published throughout the year.
The Infographic above (PDF) shows the latest update from 2022. The PDF of report is available here.
Selective extract from the executive summary as follows:
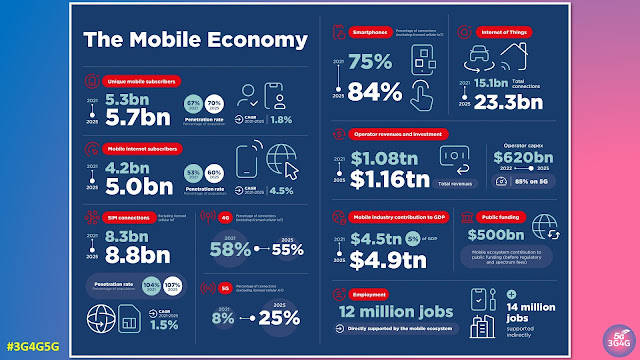
The mobile industry has been instrumental in extending connectivity to people around the world. In 2021, the number of mobile internet subscribers reached 4.2 billion people globally. Operators’ investments in network infrastructure over the last decade have helped to shrink the coverage gap for mobile broadband networks from a third of the global population to just 6%. But although the industry continues to invest in innovative solutions and partnerships to extend connectivity to still underserved and far-flung communities, the adoption of mobile internet services has not kept pace with the expansion of network coverage. This has resulted in a significant usage gap. In 2021, the usage gap stood at 3.2 billion people, or 41% of the global population.
The reasons for the usage gap are multifaceted and vary by region, but they generally relate to a lack of affordability, relevance, knowledge and skills, in addition to safety and security concerns. Furthermore, the barriers to mobile internet adoption are particularly acute among certain segments of the population, including women, the elderly, those in rural areas and persons with disabilities – or a combination thereof. Addressing the usage gap for these key groups will extend the benefits of the internet and digital technology to more people in society, and will require concerted efforts by a broad range of stakeholders working together with mobile operators and other ecosystem players, such as device manufacturers and digital content creators.
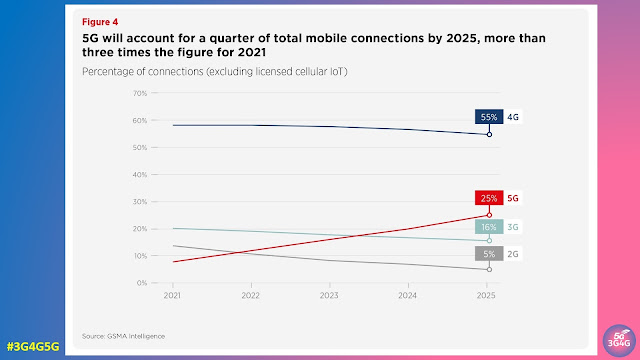
5G adoption continues to grow rapidly in pioneer markets, with the total number of connections set to reach 1 billion in 2022. Momentum has been boosted by a number of factors, including the economic recovery from the pandemic, rising 5G handset sales, network coverage expansions and overall marketing efforts by mobile operators. Meanwhile, a new wave of 5G rollouts in large markets with modest income levels (such as Brazil, Indonesia and India) could further incentivise the mass production of more affordable 5G devices, which in turn could further bolster subscriber growth. By the end of 2025, 5G will account for around a quarter of total mobile connections and more than two in five people around the world will live within reach of a 5G network.
4G still has room to grow in most developing markets, particularly in SubSaharan Africa, where 4G adoption is still below a fifth of total connections and operators are stepping up efforts to migrate existing 2G and 3G customers to 4G networks. However, rising 5G adoption in leading markets, such as China, South Korea and the US, means that 4G adoption on a global level is beginning to decline. Globally, 4G adoption will account for 55% of total connections by 2025, down from a peak of 58% in 2021.
By the end of 2021, 5.3 billion people subscribed to mobile services, representing 67% of the global population. In a growing number of markets, most adults now own a mobile phone, meaning that future growth will come from younger populations taking out a mobile subscription for the first time. Over the period to 2025, there will be an additional 400 million new mobile subscribers, most of them from Asia Pacific and Sub-Saharan Africa, taking the total number of subscribers to 5.7 billion (70% of the global population).
In 2021, mobile technologies and services generated $4.5 trillion of economic value added, or 5% of GDP, globally. This figure will grow by more than $400 billion by 2025 to nearly $5 trillion as countries increasingly benefit from the improvements in productivity and efficiency brought about by the increased take-up of mobile services. 5G is expected to benefit all economic sectors of the global economy during this period, with services and manufacturing experiencing the most impact.
You can download all reports from here.
For anyone interested in keeping a track of which 2G/3G networks are undergoing sunset, you can follow my Twitter thread that lists all the networks I become aware of
Orange is shutting down some 2G/3G networks in Europe, African opcos won't be affected. In summary:
— Zahid Ghadialy (@zahidtg) March 5, 2022
* France: 2G shutdown 2025, 3G sunset 2028
* Rest of Europe: 3G switch off by 2025 & 2G latest by 2030#2G #3G #3G4G5G #2G3Gshutdownhttps://t.co/3iYF93MWej
Related Posts:
- The 3G4G Blog: Are there 50 Billion IoT Devices yet?
- The 3G4G Blog: The Status of 5G Standalone (5G SA) Networks - March 2021
- The 3G4G Blog: Real-life 5G Use Cases for Verticals from China
- The 3G4G Blog: When will 2G & 3G be switched off now that 5G is here?
- The 3G4G Blog: Can KaiOS accelerate the transition from 2G / 3G to 4G?



No comments:
Post a Comment