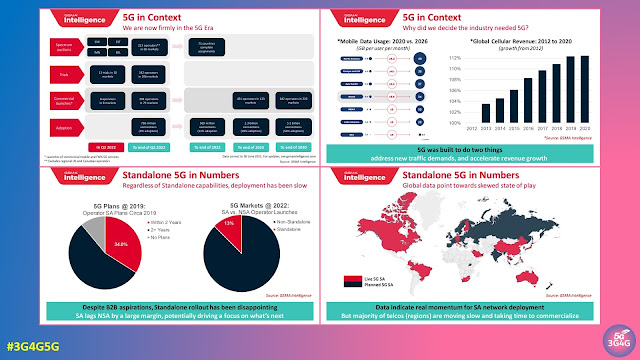
The Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) recently released its "Regional Spotlight Africa – October 2024" report. It tracks 604 public mobile networks across North and Sub-Saharan Africa, including LTE, LTE-Advanced, 5G, and fixed wireless access networks. The report gives an up-to-date view of 4G and 5G deployment in Africa, using the latest data and insights from GSA's various reports on mobile networks and satellite services.
Africa has seen major progress in telecommunications in recent years. The expansion of 4G LTE networks has improved data speeds, enhanced connectivity, and supported the spread of mobile broadband services. Looking ahead, 5G technology promises even faster speeds, lower latency, and stronger security, opening the door to new possibilities in connectivity.
The report covers key areas of mobile network development, such as:
- The current state of LTE and 5G rollouts
- LTE-Advanced advancements
- 5G standalone networks
- The growth of private networks
- Phasing out 2G and 3G technologies
- Progress in satellite services
Alongside the report, GSA hosted a regional webinar where the research team shared insights on:
- The status of LTE and LTE-Advanced in Africa and how it compares globally
- Whether 5G development is being delayed by ongoing LTE rollouts and older devices
- Recent spectrum auctions and assignments
- The transition from 2G and 3G networks
- The potential for satellite non-terrestrial (NTN) services in Africa and how operators are responding
The webinar video is available below.
Related Posts:
- Private Networks Technology Blog: Private Networks Growth in APAC
- The 3G4G Blog: GSA's Updates on Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) Numbers
- Operator Watch Blog: The Status of Mobile Networks in Latin America
- Connectivity Technology Blog: LTE vs 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)